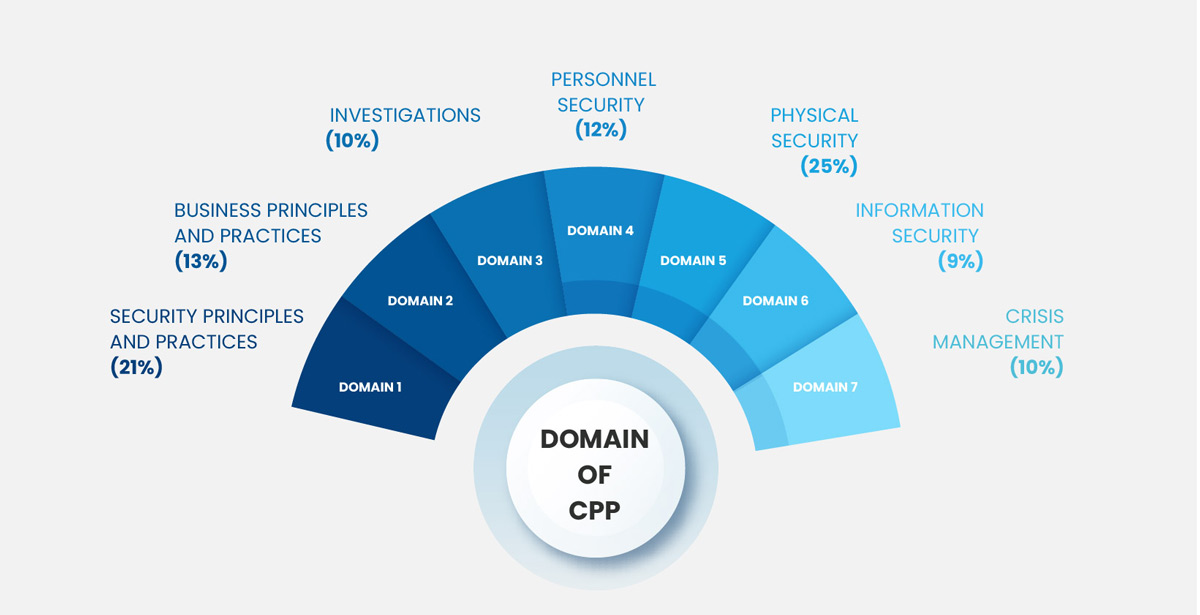
Domain 1: Security Principles and Practices (22%)
1: Plan, develop, implement, and manage the organization’s security program to protect the organization’s assets. Knowledge of:
- Principles of planning, organization, and control
- Security theory, techniques, and processes (e.g., artificial intelligence, IoT)
- Security industry standards (e.g., ASIS/ISO)
- Continuous assessment and improvement processes
- Cross-functional organizational collaboration
- Enterprise Security Risk Management (ESRM)
2: Develop, manage, or conduct the security risk assessment process. Knowledge of:
- Quantitative and qualitative risk assessments
- Vulnerability, threat, and impact assessments
- Potential security threats (e.g., “all hazards,” criminal activity, terrorism, consequential)
3: Evaluate methods to improve the security program on a continuous basis through the use of auditing, review, and assessment. Knowledge of:
- Cost-benefit analysis methods
- Risk management strategies (e.g., avoid, assume/accept, transfer, spread)
- Risk mitigation techniques (e.g., technology, personnel, process, facility design)
- Data collection and trend analysis techniques
4: Develop and manage professional relationships with external organizations to achieve security objectives. Knowledge of:
- Roles and responsibilities of external organization and agencies
- Methods for creating effective working relationships
- Techniques and protocols of liaison
- Local and national public/private partnerships
5: Develop, implement, and manage workforce security awareness programs to achieve organizational goals and objectives. Knowledge of:
- Training methodologies
- Communication strategies, techniques, and methods
- Awareness program objectives and program metrics
- Elements of a security awareness program (e.g., roles and responsibilities, physical risk, communication risk, privacy)
Domain 2: Business Principles and Practices (15%)
1: Develop and manage budgets and financial controls to achieve fiscal responsibility. Knowledge of:
- Principles of management accounting, control, audits, and fiduciary responsibility
- Business finance principles and financial reporting
- Return on Investment (ROI) analysis
- The lifecycle for budget planning purposes
2: Develop, implement, and manage policies, procedures, plans, and directives to achieve organizational objectives. Knowledge of:
- Principles and techniques of policy/procedures development
- Communication strategies, methods, and techniques
- Training strategies, methods, and techniques
- Cross-functional collaboration
- Relevant laws and regulations
3: Develop procedures/techniques to measure and improve organizational productivity. Knowledge of:
- Techniques for quantifying productivity/metrics/key performance indicators (KPI)
- Data analysis techniques and cost-benefit analysis
- Improvement techniques (e.g., pilot/beta testing programs, education, training)
4: Develop, implement, and manage security staffing processes and personnel development programs in order to achieve organizational objectives. Knowledge of:
- Interview techniques for staffing
- Candidate selection and evaluation techniques
- Job analysis processes
- Pre-employment background screening
- Principles of performance evaluations, 360 reviews, and coaching/mentoring
- Interpersonal and feedback techniques
- Training strategies, methodologies, and resources
- Retention strategies and methodologies
- Talent management and succession planning
5: Monitor and ensure an acceptable ethical climate in accordance with regulatory requirements and organizational culture. Knowledge of:
- Governance standards
- Guidelines for individual and corporate behavior
- Generally accepted ethical principles
- Confidential information protection techniques and methods
- Legal and regulatory compliance
6: Develop performance requirements and contractual terms for security vendors/suppliers. Knowledge of:
- Key concepts in the preparation of requests for proposals and bid reviews/evaluations
- Service Level Agreement (SLA) terms, metrics, and reporting
- Contract law, indemnification, and liability insurance principles
- Monitoring processes to ensure that organizational needs and contractual requirements are being met
Domain 3: Investigations (9%)
1: Identify, develop, implement, and manage investigative operations. Knowledge of:
- Principles and techniques of policy and procedure development
- Organizational objectives and cross-functional collaboration
- Types of investigations (e.g., incident, misconduct, compliance, due diligence)
- Internal and external resources to support investigative functions
- Report preparation for internal/external purposes and legal proceedings
- Laws pertaining to developing and managing investigative programs
2:Manage or conduct the collection, preservation, and disposition of evidence to support investigative actions. Knowledge of:
- Protection/preservation of crime scene
- Evidence collection techniques
- Requirements of chain of custody
- Methods for preservation/disposition of evidence
- Laws pertaining to the collection, preservation, and disposition of evidence
3:Manage or conduct surveillance processes. Knowledge of:
- Surveillance and counter-surveillance techniques
- Technology/equipment and personnel to conduct surveillance (e.g., Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS), robotics)
- Laws pertaining to managing surveillance processes
4:Manage and conduct investigations requiring specialized tools, techniques, and resources. Knowledge of:
- Financial and fraud related crimes
- Intellectual property and espionage crimes
- Crimes against property (e.g., arson, vandalism, theft, sabotage)
- Cybercrimes (e.g., distributed denial of service (DDoS), phishing, ransomware)
- Crimes against persons (e.g., workplace violence, human trafficking, harassment)
5:Manage or conduct investigative interviews. Knowledge of:
- Interview and interrogation techniques
- Techniques for detecting deception
- Non-verbal communication and cultural considerations
- Rights of interviewees
- Required components of written statements
- Legal considerations pertaining to managing investigative interviews
6:Provide support to legal counsel in actual or potential criminal or civil proceedings. Knowledge of:
- Statutes, regulations, and case law governing or affecting the security industry and the protection of people, property, and information
- Criminal law and procedures
- Civil law and procedures
- Employment law (e.g., confidential information, wrongful termination, discrimination, harassment)
Domain 4: Personnel Security (11%)
1:Develop, implement, and manage background investigation processes for hiring, promotion, and retention of individuals. Knowledge of:
- Background investigations and personnel screening techniques
- Quality and types of information sources (e.g., open source, social media, government databases, credit reports)
- Screening policies and guidelines
- Laws and regulations pertaining to personnel screening
2:Develop, implement, manage, and evaluate policies and procedures to protect individuals in the workplace against human threats (e.g., harassment, violence, active assailant). Knowledge of:
- Protection techniques and methods
- Threat assessment
- Prevention, intervention, and response tactics
- Educational and awareness program design and implementation
- Travel security (e.g., flight planning, global threats, consulate services, route selection, contingency planning)
- Industry/labor regulations and applicable laws
- Organizational efforts to reduce employee substance abuse
3:Develop, implement, and manage executive protection programs. Knowledge of:
- Executive protection techniques and methods
- Threat analysis
- Liaison and resource management techniques
- Selection, costs, and effectiveness of proprietary and contract executive protection personnel
Domain 5: Physical Security (16%)
1:Conduct facility surveys to determine the current status of physical security. Knowledge of:
- Security protection equipment and personnel (e.g., Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS), robotics)
- Survey techniques (e.g., document review, checklist, onsite visit, stakeholder interviews)
- Building plans, drawings, and schematics
- Risk assessment techniques
- Gap analysis
2:Select, implement, and manage physical security strategies to mitigate security risks. Knowledge of:
- Fundamentals of security system design
- Countermeasures (e.g., policies, technology, procedures)
- Budgetary projection development process (e.g., technology, hardware, labor)
- Bid package development and evaluation process
- Vendor qualification and selection process
- Testing procedures and final acceptance (e.g., commissioning, factory acceptance test)
- Project management techniques
- Cost-benefit analysis techniques
- Labor-technology relationship
3: Assess the effectiveness of physical security measures by testing and monitoring. Knowledge of:
- Protection personnel, hardware, technology, and processes
- Audit and testing techniques (e.g., operation testing)
- Predictive, preventive, and corrective maintenance
Domain 6: Information Security (14%)
1:Conduct surveys to evaluate the current status of information security programs. Knowledge of:
- Survey techniques
- Quantitative and qualitative risk assessments
- Risk mitigation strategies (e.g., technology, personnel, process, facility design)
- Cost-benefit analysis methods
- Protection technology, security threats equipment, and procedures (e.g., interoperability)
- Information security threats
- Integration of facility and system plans, drawings, and schematics
2:Develop policies and procedures to ensure information is evaluated and protected against vulnerabilities and threats. Knowledge of:
- Principles of information security management
- Information security theory and terminology
- Information security industry standards (e.g., ISO, PII, PCI)
- Laws and regulations regarding records management including collection, retention, legal holds, and disposition practices (e.g., General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), biometric information)
- Practices to protect proprietary information and intellectual property
- Information protection measures including security processes, physical access systems, and data management
3:Implement and manage an integrated information security program. Knowledge of:
- Information security including confidentiality, integrity, and availability
- Information security systems methodology
- Authentication techniques (e.g., multi-factor, biometrics)
- Continuous evaluation and improvement programs
- Ethical hacking and penetration testing techniques and practices
- Encryption and data masking techniques (e.g., cryptography)
- Systems integration techniques (e.g., interoperability, licensing, networking)
- Cost-benefit analysis methodology
- Project management techniques
- Budget review process (e.g., system development lifecycle)
- Vendor evaluation and selection process
- Final acceptance and testing procedures
- Protection technology and forensic investigations
- Training and awareness programs to mitigate threats and vulnerabilities (e.g., phishing, social engineering, ransomware, insider threats)
Domain 7: Crisis Management (13%)
1:Assess and prioritize threats to mitigate potential consequences of incidents. Knowledge of:
- Threats by type, likelihood of occurrence, and consequences
- “All hazards” approach to assessing threats (e.g., natural disaster, chemical, biological, radiological, nuclear, explosives (CBRNE))
- Cost-benefit analysis
- Mitigation strategies
- Risk management and business impact analysis methodology
- Business continuity standards (e.g., ASIS ORM.1, ISO 22301)
1:Prepare and plan how the organization responds to incidents. Knowledge of:
- Resource management techniques (e.g., mutual aid agreements, MOUs)
- Emergency planning techniques
- Triage and damage assessment techniques
- Communication techniques and notification protocols (e.g., interoperability, common operating terms, emergency notification system)
- Training and exercise techniques (e.g., tabletop and full-scale exercises)
- Emergency operations center (EOC) concepts and design
- Primary roles and duties in an Incident Command Structure (ICS) (e.g., information dissemination, liaison, Public Information Officer (PIO))
1:Respond to and manage an incident. Knowledge of:
- Resource allocation
- Emergency Operations Centre (EOC) management principles and practices
- Incident management systems and protocols
1:Manage incident recovery and resumption of operations. Knowledge of:
- Resource management
- Short- and long-term recovery strategies
 Read Reviews
Read Reviews





 5th Sep: Weekend
5th Sep: Weekend 




 The training was awesome. Helped me clear my concepts and also reduced my preparation time to 1/3rd. Thank you, trainer, for all your dedication to bring your gladiators to pace.
The training was awesome. Helped me clear my concepts and also reduced my preparation time to 1/3rd. Thank you, trainer, for all your dedication to bring your gladiators to pace.






 Certified & Experienced Instructors
Certified & Experienced Instructors Post Training Support
Post Training Support Customized Training
Customized Training Flexible Schedule
Flexible Schedule Access to Recorded Sessions
Access to Recorded Sessions 



 1800-843-7890 (India)
1800-843-7890 (India) 
