Top Deep Learning Algorithms
Deep learning has transformed the world of Artificial Intelligence (AI), powering everything from voice assistants and self-driving cars to medical diagnosis and financial predictions. But behind these groundbreaking advancements lie powerful algorithms, the backbone of deep learning models.

Deep learning algorithms are reshaping cybersecurity, from detecting malware with high accuracy to identifying anomalies in vast networks. But with so many architectures available, which ones are the most effective? In this article, we explore the most widely used deep learning algorithms in cybersecurity, highlighting their unique strengths and applications.
What is Deep Learning?
Deep learning is a subset of Machine Learning (ML) that utilizes Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) with multiple layers to process and extract complex patterns from large amounts of data. It is particularly effective in cybersecurity applications, where it helps in threat detection, anomaly detection, intrusion prevention, and malware classification. By leveraging deep learning algorithms, cybersecurity professionals can develop intelligent systems to identify and mitigate cyber threats in real time.
The Design of an ANN is inspired by the human brain. Each artificial neuron resembles a Biological neuron (nerve cell). Just like its biological counterpart, an artificial neuron also receives signals through its input layer, processes them in the hidden layer, and transmits results through the output layer.
Most Popular Deep Learning Algorithms
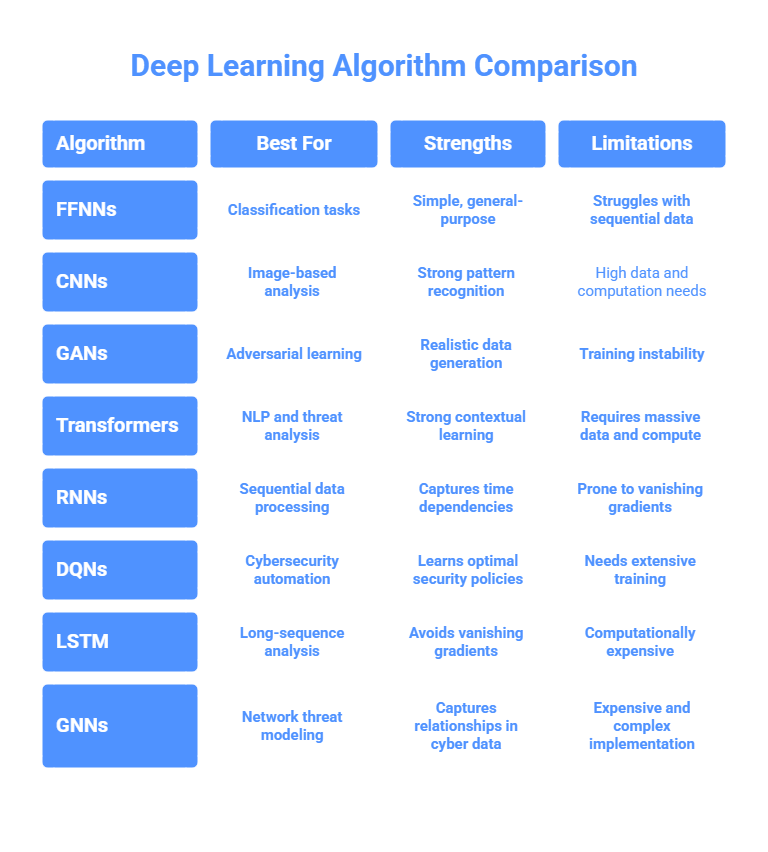
1. Feedforward Neural Networks (FFNNs)
FFNNs are the most basic type of artificial neural network, where data flows in a single direction, forward, from input to output, without cycles or loops. They consist of multiple layers: an input layer, hidden layers (One or More), and an output layer.
Key Features
- Uses activation functions (e.g., ReLU, Sigmoid) to introduce non-linearity. Non-linearity is important as it allows the network to learn and handle much more complicated patterns. If an artificial neuron has this function activated, it will forward the data to the next layer.
- Trained using backpropagation and gradient descent.
Cybersecurity Applications
- Malware Detection: Classifies files as malicious or benign based on feature extraction.
- Anomaly Detection: Identifies patterns in network traffic to detect irregular activities.
2. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
CNNs are specialized neural networks for processing spatial data. By utilizing convolutional layers to identify patterns in input data, they excel in image and pattern recognition tasks.
Key Features
- Utilizes convolutional layers with filters to extract features.
- Employs pooling layers (max pooling, average pooling) to reduce dimensionality.
- Effective in feature learning and pattern recognition.
Cybersecurity Applications
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): CNNs process network traffic patterns and detect intrusions.
- Phishing Detection: Classifies phishing websites and fraudulent images based on visual cues.
3. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
GANs are machine learning models composed of two competing neural networks—a generator and a discriminator—that collaborate to generate realistic data.
Key Features
- Generator creates synthetic data samples by observing real data patterns and mimicking it.
- Discriminator evaluates whether samples are real or fake.
- Adversarial training improves data authenticity.
Cybersecurity Applications
- Adversarial Attack Simulation: Generates slightly altered versions of real data, which is used to trick the model. This reveals vulnerabilities in how the system makes decisions (like penetration testing on AI systems). This process helps strengthen the model’s defenses against similar real-world attacks.
- Synthetic Data Generation: Creates datasets for cybersecurity training and testing.
4. Transformer Networks
Transformers, including models like BERT and GPT, utilize self-attention mechanisms to process sequences in parallel rather than sequentially. They excel in NLP and contextual learning.
Key Features
- Uses self-attention mechanisms to weigh input relevance dynamically.
- Processes entire sequences simultaneously, enhancing efficiency.
- Forms the backbone of NLP models like BERT and GPT.
Cybersecurity Applications
- Threat Intelligence Analysis: Processes textual threat reports to extract actionable insights.
- Automated Security Log Analysis: Detects patterns in security logs for anomaly detection.
5. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs)
RNNs are designed for sequential data processing, with recurrent connections allowing information to persist over time. They are useful for time-series and sequential predictions.
Key Features
- Maintains internal memory (hidden states) to capture temporal dependencies.
- Trained using backpropagation through time (BPTT).
- Suffers from vanishing gradient issues in long sequences.
Cybersecurity Applications
- Log Analysis: Detects anomalies in system and network logs over time.
- Fraud Detection: Tracks transactional sequences to identify fraudulent activity.
6. Deep Q-Network (DQN)
DQN is a reinforcement learning algorithm that utilizes deep learning to approximate Q-values for optimal decision-making.
Key Features
- Uses deep neural networks to approximate Q-values.
- Employs experience replay to stabilize training.
- Optimizes decision-making in dynamic environments.
Cybersecurity Applications
- Automated Penetration Testing: Learns optimal attack strategies to test security defenses.
- Adaptive Threat Response: Dynamically adjusts security policies based on attack patterns.
7. Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM)
LSTM is a specific type of RNN developed to address the vanishing gradient problem. They use memory cells to retain information over long sequences.
Key Features
- Uses gates (input, forget, and output) to regulate information flow.
- Retains information over long sequences without degradation.
- Effective for time-series and sequential analysis.
Cybersecurity Applications
- Insider Threat Detection: Monitors user behavior over time to identify anomalies.
- Botnet Detection: Tracks network traffic sequences to detect botnet activity.
8. Graph Neural Networks (GNNs)
GNNs are built to operate on graph-structured data, making them effective in modeling relationships and dependencies between nodes in a network.
Key Features
- Captures relationships and dependencies in graph data.
- Uses message-passing mechanisms to aggregate information.
- Suitable for analyzing complex interconnected systems.
Cybersecurity Applications
- Attack Graph Analysis: Identifies vulnerabilities and attack paths in network structures.
- Fraud Detection: Detects fraudulent activities by analyzing transaction networks.
Conclusion
ANNs are of various types. Deep learning algorithms are nothing but different types of ANNs. Each deep learning algorithm has unique strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for different cybersecurity applications. CNNs and GANs excel at pattern recognition and adversarial learning, while RNNs, LSTMs, and Transformers are well-suited for sequential threat analysis. GNNs provide advanced capabilities for modeling cyber networks, and DQNs enable AI-driven cyber defense automation.
AI-Powered Cybersecurity Training with InfosecTrain
InfosecTrain‘s AI-Powered Cybersecurity Training helps individuals understand deep learning algorithms by providing hands-on experience with AI-driven security solutions. The course covers key deep learning models like CNNs, RNNs, and GANs, and their applications in threat detection, anomaly detection, and malware analysis. Through practical labs and expert guidance, learners gain real-world cybersecurity skills using AI techniques.
TRAINING CALENDAR of Upcoming Batches For AI-Powered Cybersecurity Training Course Online
| Start Date | End Date | Start - End Time | Batch Type | Training Mode | Batch Status | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14-Mar-2026 | 12-Apr-2026 | 19:00 - 23:00 IST | Weekend | Online | [ Open ] | |
| 04-Apr-2026 | 10-May-2026 | 09:00 - 13:00 IST | Weekend | Online | [ Open ] | |
| 02-May-2026 | 07-Jun-2026 | 19:00 - 23:00 IST | Weekend | Online | [ Open ] |

