Threat Hunting vs. Threat Detection
As cyber threats become more common, relying on conventional tools such as firewalls, antivirus software, or even SIEM platforms is insufficient to address the complexity of today’s risks. Threats are constantly evolving, with attackers adopting increasingly advanced Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs). This is where threat hunting and threat detection come into play. Both are essential for building a robust cybersecurity strategy, but they serve distinct roles.

Understanding these concepts is like understanding the difference between proactive and reactive defenses. Both are critical, but when combined, they form a robust security posture capable of not just mitigating risks but actively countering adversaries. Let’s dive deeper into threat hunting and threat detection and explore their differences.
What Is Threat Detection?
Threat detection focuses on identifying malicious activities or anomalies within an organization’s network or systems. It uses predefined rules, algorithms, and machine learning models to monitor and alert suspicious behavior.
How it works?
- Rule-Based Alerts: Detection systems rely heavily on predefined rules and Indicators of Compromise (IOCs). For example, if an employee logs in from a known IP address in the morning and then another login is detected from a foreign country within minutes, the system will flag it as suspicious.
- Tools: Security tools like Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR), and SIEM platforms form the backbone of threat detection efforts.
- Reactive in Nature: Threat detection is typically a reactive approach. It focuses on identifying threats after they have already entered the network or started their activity.
Core Technologies
- SIEM (Security Information and Event Management): Collects and analyzes log data in real-time.
- EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response): Monitors endpoints for suspicious activity and provides response capabilities.
- IDS/IPS (Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems): Identifies and blocks unauthorized access attempts.
Key Advantage:
Threat detection automates the process of identifying known threats, enabling a much faster response to incidents. However, it has limitations when it comes to uncovering new or unknown threats, leading us to threat hunting.
What is Threat Hunting?
Threat hunting is a proactive approach where Security Analysts actively search for potential threats, even before any alarms are raised. It’s the equivalent of having a detective investigate a crime scene—except in this case, the crime hasn’t happened yet.
How it Works?
- Hypothesis-Driven Exploration: Threat Hunters rely on hypotheses about potential attack vectors. For example, a hypothesis could be: “If an attacker compromises an admin account, what paths could they take to escalate privileges further?”
- Behavioral Analysis: Unlike threat detection, hunting doesn’t depend solely on IOCs. It leverages behavioral patterns, threat intelligence, and advanced analytics to uncover hidden adversaries.
- Human-Centric: While tools and automation play a role, threat hunting leans heavily on the expertise of Security Analysts who can think like attackers.
Core Technologies:
- Threat Intelligence Platforms: Provide information on emerging Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs).
- Network Traffic Analysis (NTA): Examines network flows to identify abnormal patterns.
- Forensic Tools: Enable deep investigation into system behaviors and artifacts.
Key Differences: Threat Hunting vs. Threat Detection
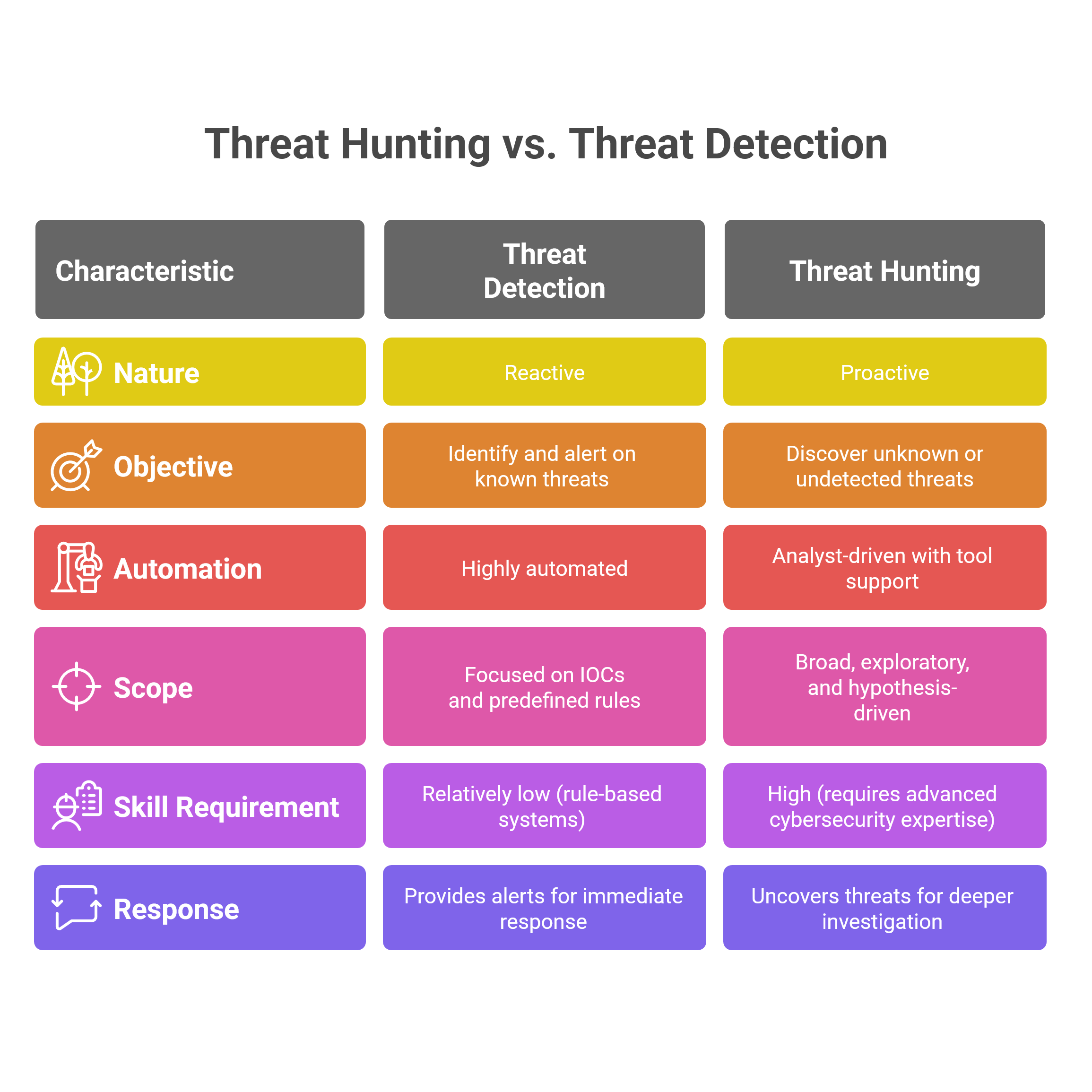
Common Myths About Threat Hunting and Detection
Despite their importance, several misconceptions surround these practices. Let’s debunk a few:
- “Threat Hunting Replaces Threat Detection” No, it doesn’t. Threat hunting is not a replacement but an enhancement. Threat detection supplies the data and context that Threat Hunters rely on to develop hypotheses and investigate potential unknown threats.
- “Automation Makes Hunting Obsolete” While AI and automation can aid threat hunting, they cannot replace the creativity and intuition of human analysts. Cybercriminals are humans, after all, and they’re adept at finding new ways to bypass automated defenses.
- “Detection Alone Is Enough” Relying solely on detection systems leaves you blind to sophisticated attacks, especially those that don’t match known patterns. Threat hunting fills this critical gap.
Implementing Threat Hunting and Detection
Organizations must integrate both strategies to create a balanced and effective security posture. Here are some actionable tips:
1. Invest in the Right Tools
- Deploy tools like SIEM, EDR, and network traffic analysis solutions for detection.
- Use advanced analytics platforms to support threat hunting efforts.
2. Build a Skilled Team
- Hire analysts with experience in both proactive threat hunting and reactive incident response.
- Provide continuous training to keep up with the evolving threat landscape.
3. Leverage Threat Intelligence
- Incorporate threat intelligence feeds into your detection and hunting workflows.
- Use insights from hunting activities to enhance detection systems.
4. Foster Collaboration
- Create a feedback loop where hunters and detectors share insights.
- Use shared findings to improve overall security policies and procedures.
SOC Analyst with InfosecTrain
Threat hunting and threat detection are two sides of the same coin. While they operate differently, they share the common goal of safeguarding your organization from adversaries. By mastering their differences and integrating their strengths, you can develop a cybersecurity strategy that’s resilient, adaptable, and ready to face the future.
If you’re ready to elevate your skills and stay ahead in the evolving cybersecurity environment, InfosecTrain offers industry-leading training in SOC Analyst and Advanced Cyber Threat Hunting, and DFIR (Digital Forensics and Incident Response). Equip yourself with the tools, techniques, and expertise needed to identify, hunt, and mitigate cyber threats like a pro. Start your journey to becoming a Cybersecurity Expert today and gain the confidence to secure any environment from tomorrow’s challenges.
TRAINING CALENDAR of Upcoming Batches For SOC Analyst
| Start Date | End Date | Start - End Time | Batch Type | Training Mode | Batch Status | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14-Mar-2026 | 03-May-2026 | 19:00 - 23:00 IST | Weekend | Online | [ Open ] |

