Azure RBAC vs. Azure AD Roles

What is Azure RBAC (Role-Based Access Control)?
Azure RBAC is a system within Microsoft Azure that allows organizations to securely manage and control access to their Azure resources. With Azure RBAC, administrators can assign permissions at different levels, such as subscriptions, resource groups, or individual resources (e.g., virtual machines, storage accounts), to specify who can perform specific actions. This approach ensures that users, applications, and groups have precisely the permissions needed for their roles, minimizing excessive access and promoting a secure, least-privilege environment.
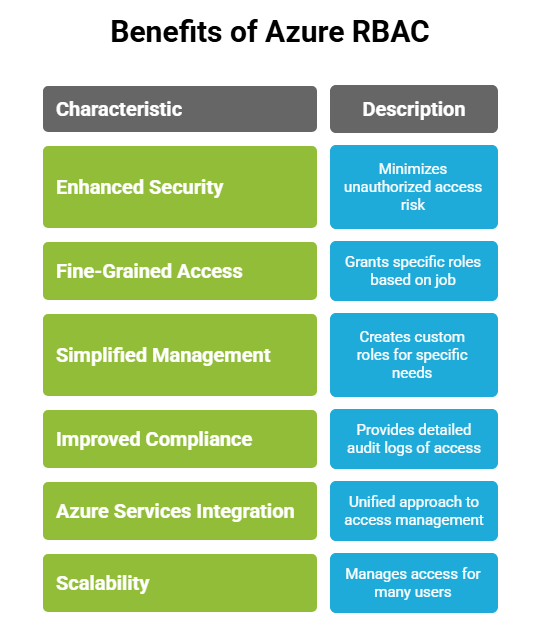
Common Use Cases
- Assigning access for users to manage or view resources, like granting Virtual Machine Contributor access to DevOps engineers at the resource group level.
- Restricting access to specific resources for teams by using custom roles or by assigning a limited set of permissions.
What are Azure AD (Active Directory) Roles?
Azure AD roles are predefined sets of permissions in Microsoft Azure designed to control access to Azure AD resources, primarily for identity and access management tasks within an organization. Unlike Azure RBAC roles, which govern permissions to Azure resources, Azure AD roles focus specifically on managing user identities, groups, applications, and access policies within the Azure AD tenant.
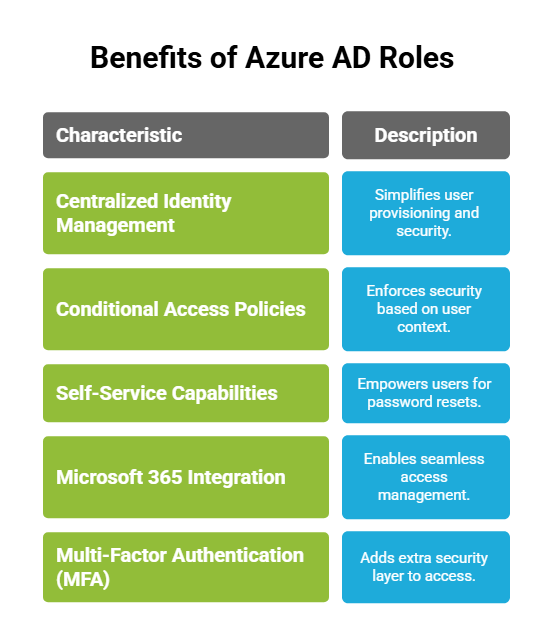
Common Use Cases
- Assigning Global Administrator rights to IT admins to oversee the entire Azure AD tenant.
- Granting User Administrator permissions to allow HR or support teams to manage users, reset passwords, and handle onboarding/offboarding.
- Assigning Application Administrator rights for managing enterprise applications within the directory.
Key Difference Between Azure RBAC and Azure AD Roles
| Feature | Azure RBAC Roles | Azure AD Roles |
| Primary Purpose | Implement the principle of least privilege, allowing users or applications only the permissions necessary to perform their job functions without over-permission. | Govern the access and management of the identity infrastructure, which is crucial for securing access across an organization. |
| Scope | Applies at Azure resource levels: subscription, resource group, or individual resource. | Applies at the Azure AD tenant level and affects all users, groups, and AD resources within that tenant. |
| Types of Roles | Owner: Full access to all resources and permissions.
Contributor: Manage resources but no access control. Reader: View-only access to resources. |
Global Administrator: Full access to Azure AD and some subscription settings.
User Administrator: Manage user and group settings. Application Administrator: Manage app registrations and enterprise apps. |
| Permissions Granularity | Fine-grained, offering control over specific resources, actions, and levels within Azure services. | Coarse-grained, focusing on administrative tasks within Azure AD, like managing users, groups, and app registrations. |
| Inheritance and Propagation | Roles are inherited from higher levels, allowing propagation from subscriptions to lower resource levels. | No inheritance; roles are directly assigned and applied tenant-wide across Azure AD. |
| Supported Services | Only affects Azure resources (VMs, compute, storage, networks, etc.) | Primarily applied to Azure AD and Microsoft 365 services (Exchange Online, SharePoint Online, etc.) |
| Compliance and Auditing | Resource-level events tracked in Azure Activity Logs for auditing and monitoring access control changes. | Identity management events are audited through Azure AD logs, tracking sign-ins, role assignments, and AD-related actions. |
| Best Use Cases | Ideal for organizations that need granular control over specific Azure resources and workloads. | Best for managing identities, users, groups, and applications at the tenant level, especially in hybrid identity setups. |
| Customization | Highly customizable, allowing you to create custom roles with specific permissions tailored to specific resource management needs. | Customization is more limited than Azure RBAC. While some customizations are possible, they are primarily predefined by Microsoft to cover administrative functions for directory and identity management. |
In Conclusion
You can choose between Azure RBAC and Azure AD roles based on your access control needs. Use Azure Role-Based Access Control roles for managing permissions at the resource level, which is ideal when granting or restricting access to specific Azure resources like VMs, databases, or storage within subscriptions or resource groups. Opt for Azure AD roles when focusing on identity management, such as controlling access to user identities, groups, and applications at the directory (tenant) level. For a comprehensive approach, combine Azure RBAC for resource-specific access and Azure AD roles for secure, organization-wide identity and user management.
Azure Combo Training with InfosecTrain
Want to get a solid understanding of Azure RBAC Roles and Azure AD Roles? InfosecTrain‘s Azure Combo course provides hands-on training and expert guidance to help individuals understand these complex topics in a clear and structured way. It covers how role-based access control works across Azure resources and how Azure AD roles manage identity and directory-level permissions. Through hands-on labs, real-world scenarios, and expert-led instruction, learners gain practical skills to configure and manage access securely.
TRAINING CALENDAR of Upcoming Batches For AZ-104 & AZ-500
| Start Date | End Date | Start - End Time | Batch Type | Training Mode | Batch Status | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31-Jan-2026 | 01-Mar-2026 | 19:00 - 23:00 IST | Weekend | Online | [ Open ] |
