What is a Configuration Management Database (CMDB)?
In today’s complex IT environments, keeping track of what’s running where and how everything is connected can feel like piecing together a puzzle blindfolded. That is where a Configuration Management Database (CMDB) comes in. It acts as the central hub for storing and managing detailed information about every asset, service, and dependency in your infrastructure.

In this post, we’ll break down what a CMDB is, why it matters, and its key features.
What is CMDB?
A Configuration Management Database (CMDB) is a centralized repository that stores detailed information about all IT assets and Configuration Items (CIs) within an organization, along with their relationships. These include:
- Servers
- Applications
- Databases
- Network devices
- Cloud assets
- Containers
- Software versions
- Services
- People (users, owners)
- Documentation
- SLAs
- Security controls
Key Purpose
- To give a real-time, accurate picture of your IT environment.
- To support change management, incident response, security analysis, and compliance auditing.
Importance of Configuration Management Database (CMDB)
Here are the key benefits of Configuration Management Database (CMDB):
1. Central Source of Truth: A CMDB holds detailed, structured data about your IT assets and their relationships:
- What do we have?
- Where is it running?
- Who owns it?
- How is it connected?
This eliminates tribal knowledge and reduces the risk of misinformed decisions.
2. Impact Analysis and Change Control: Before you roll out a patch, a new version, or a config change, you need to know:
- What systems will this affect?
- Will it break a downstream service?
- Are there SLAs or compliance risks?
A good CMDB maps dependencies, preventing outages and speeding up approvals.
3. Security and Compliance: Security isn’t just about scanning—it’s about context. A CMDB helps you:
- It maps vulnerabilities to exact assets and environments.
- It tracks unpatched software lives, what it’s connected to, and who to alert.
- It maintains audit trails and access logs.
- It is crucial for zero-day response, risk scoring, and attack surface reduction.
It supports frameworks such as NIST, ISO 27001, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS by making asset management and data flows transparent.
4. Improves Incident Response: When something breaks, the CMDB helps you:
- Identify affected systems instantly
- Trace issues across services or teams
- Engage the right stakeholders without delay
Cuts MTTR (Mean Time to Recovery) dramatically.
5. Supports Automation and Orchestration: Infrastructure as Code (IaC), Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD), and auto-remediation all rely on accurate, structured data. The CMDB fuels this by:
- Feeding pipelines with asset and environment metadata
- Enabling policy-as-code
- Driving automated compliance checks
6. Optimizes Costs and Resources
- It tracks what’s actually in use and what’s just sitting around.
- It prevents overprovisioning.
- It helps with license management and asset lifecycle planning.
7. Enables Strategic Decision-Making
- What services are business-critical?
- Where are the bottlenecks?
- What needs refactoring or migration?
CMDB gives you the data foundation to make smart infrastructure and investment choices.
8. Enables DevSecOps Collaboration: A shared CMDB bridges silos:
- Developers get visibility into infrastructure and service relationships
- Security gets context for risk and threat modeling
- Ops gets the full picture for monitoring and scaling
Features of a Configuration Management Database (CMDB)
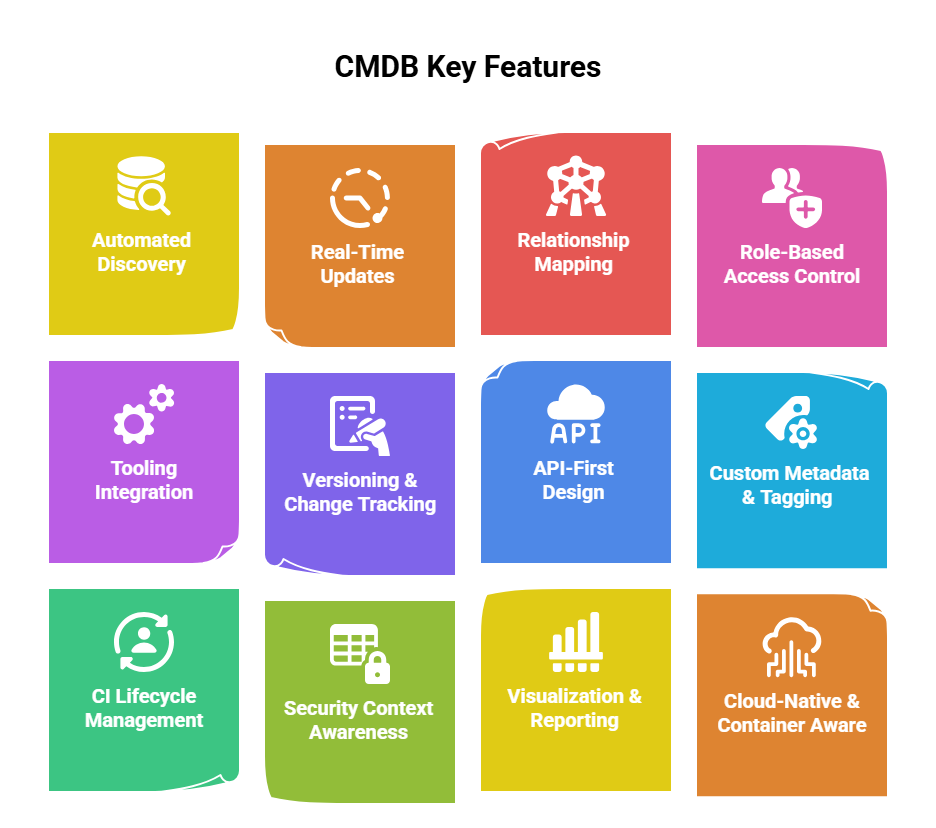
1. Automated Discovery
- Automatically finds and catalogs infrastructure, services, and applications
- Supports cloud, containers, on-prem, edge, etc.
- Reduces manual entry (which always goes stale)
2. Real-Time or Near-Real-Time Updates
- No one can afford stale data
- Keeps configuration items (CIs) up to date as changes occur
- Syncs with orchestration tools, CI/CD pipelines, and cloud APIs
3. Relationship Mapping (Dependency Visualization)
- Shows how systems are interconnected
- Helps teams understand service impact and trace failures or risks across dependencies
4. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
- Let different teams (Dev, Sec, Ops, Audit) access the data they need without exposure to everything
- Supports accountability and data governance
5. Integration with Tooling Ecosystem
- Hooks into CI/CD tools (Jenkins, GitHub Actions, etc.)
- Connects to ticketing (Jira, ServiceNow), cloud platforms, monitoring tools (Prometheus, Datadog), and security scanners (Nessus, Prisma, etc.)
- Enables full-stack automation
6. Versioning and Change Tracking
- Keeps a history of configuration changes
- Logs who did what, when, and why—critical for audit trails, rollback, and incident investigation
7. API-First Design
- Exposes data to other systems via clean, secure APIs
- Enables custom dashboards, automation scripts, and integration with third-party platforms
8. Custom Metadata and Tagging
- Enables you to tag CIs with business context (e.g., owner, environment, compliance level, criticality)
- Essential for prioritizing security and change control
9. CI Lifecycle Management
- Tracks assets across their full lifecycle: provisioning → deployment → maintenance → decommissioning
- Helps with cost tracking, compliance, and clean asset hygiene
10. Security Context Awareness
- Links CIs to vulnerabilities, compliance status, and controls
- Provides alerts or flags for insecure configurations or policy violations
11. Visualization and Reporting
- Offers dashboards, relationship graphs, impact maps, and compliance reports
- Makes it easier to communicate with both technical and non-technical stakeholders
12. Cloud-Native and Container-Aware
- Knows how to handle dynamic, ephemeral assets like containers, serverless functions, and autoscaled VMs
- Integrates with Kubernetes, Terraform, and cloud provider APIs (AWS, Azure, GCP)
DevSecOps Training with InfosecTrain
InfosecTrain’s DevSecOps Practical Training helps participants understand CMDBs by showing how they integrate into real-world security, operations, and development workflows. Through hands-on labs and guided projects, participants will learn how to map assets, track configurations, and automate compliance using tools like ServiceNow, Ansible, and CI/CD pipelines. This training bridges theory with practice, making CMDB concepts clear, relevant, and immediately applicable.
TRAINING CALENDAR of Upcoming Batches For DevSecOps
| Start Date | End Date | Start - End Time | Batch Type | Training Mode | Batch Status | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18-Apr-2026 | 23-May-2026 | 19:00 - 23:00 IST | Weekend | Online | [ Open ] |

