How to Perform a Gap Analysis for ISO 27001?
Ever feel like your organization is navigating a digital minefield? It is not an exaggeration. The cyber threat environment is not just evolving; it is exploding with new threats daily. According to IBM’s 2023 Cost of a Data Breach Report, the global average breach cost hit $4.45 million, a 15% increase over three years. Worse yet, 82% of breaches involved human error or gaps in existing controls. For many businesses, a financial hit of this magnitude is not just a setback; it is a potential knockout blow.

Beyond individual incidents, the overall cost of cybercrime is projected to inflict $10.5 trillion in damages annually by 2025. This colossal sum surpasses the GDP of many nations, highlighting the sheer scale of the challenge.
So, what is a smart business to do in the face of such an onslaught? Huddling in a corner and hoping for the best is not a strategy. This is where robust frameworks like ISO 27001 come into play, acting as a battle-tested shield for an organization’s valuable information assets.
What is an ISO 27001 Gap Analysis?
An ISO 27001 gap analysis is a comprehensive evaluation that compares an organization’s current information security practices against the specific requirements and controls outlined in the ISO 27001 standard. It functions like a detailed, strategic checklist, meticulously examining an organization’s existing security measures. It helps you:
- Identify gaps in your current Information Security Management System (ISMS).
- Prioritize actions based on risk, impact, and feasibility.
- Develop a targeted roadmap to achieve ISO 27001 compliance or certification.
The primary objective of this exercise is to identify the “gaps”, the discrepancies or shortfalls where current security practices do not meet the stipulations of ISO 27001.
Importance of Gap Analysis
Conducting a gap analysis takes time and effort, but the returns are substantial and multifaceted. The benefits extend beyond simply ticking a box on the path to certification.
- Clear Certification Roadmap: Identify what requires correction, implementation, or documentation to comply with ISO 27001 requirements.
- Save Time and Costs: Identify issues early by avoiding last-minute scrambles and rework.
- Scope Clarity: Refine the scope of your ISMS using a gap analysis to identify which areas of your organization need to be covered. This is particularly crucial for large or complex enterprises.
- Smarter Planning: Gain insight into the budget, people, and time needed to comply fully.
- Stronger Business Case: Present executives with real data and risk findings to win support and funding.
- Lower Risk Exposure: Every gap you close is one less opportunity for attackers, and each fix strengthens your real defense.
- Boost Stakeholder Trust: Show customers and partners you are serious about securing their data.
- Realistic Timeline: Set achievable targets based on the actual size of your gaps.
Practical Steps for Conducting ISO 27001:2022 Gap Analysis
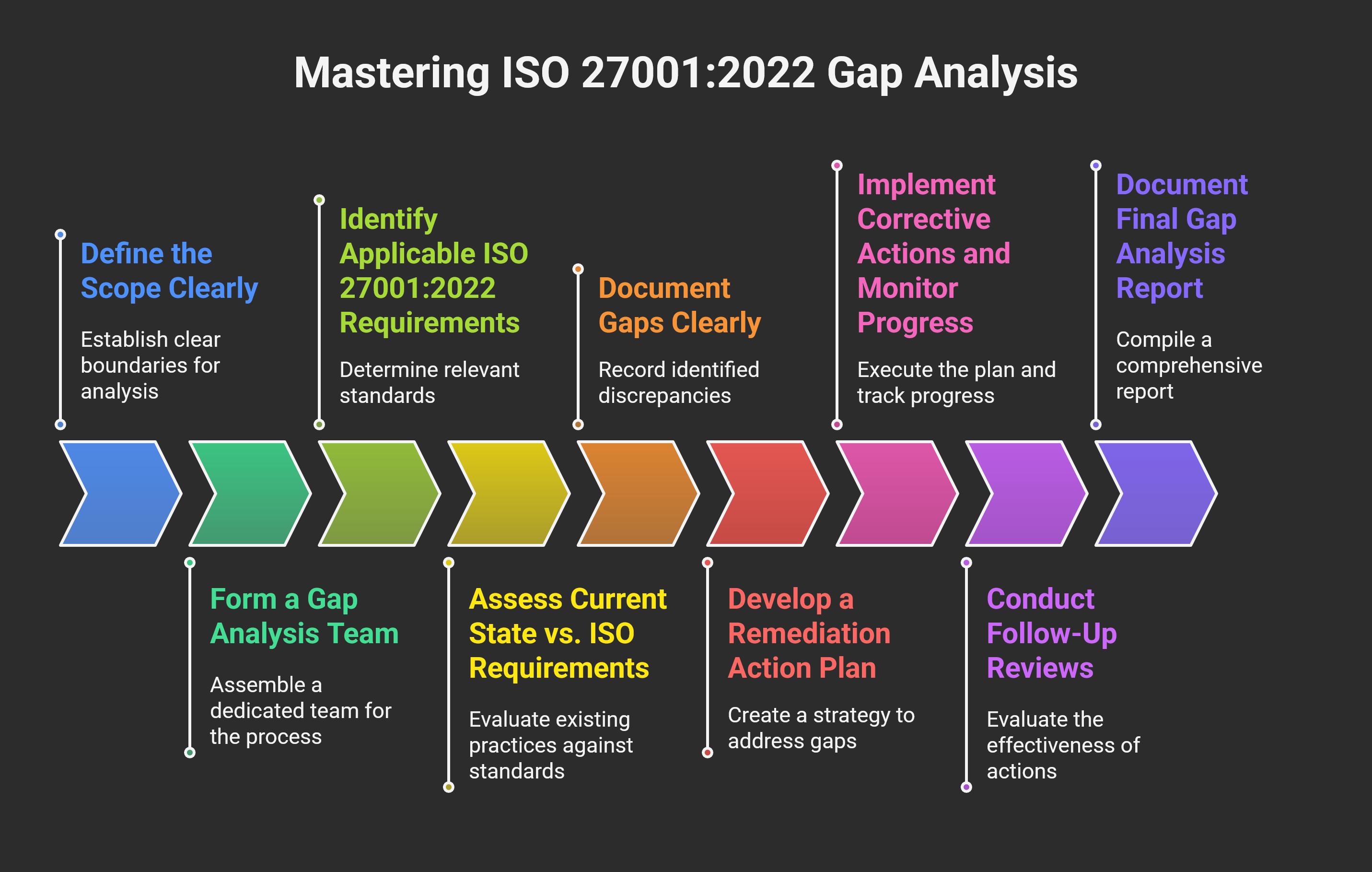
Step 1: Define the Scope Clearly
You know, starting any big project without a clear map is like setting sail without a compass. You might end up somewhere, but is it where you intended to go? Absolutely not. That is why Step 1, defining your scope, is not just a formality; it is the bedrock of your entire gap analysis. Scope includes:
- IT department (servers, networks, databases)
- HR processes (background checks, employee onboarding)
- Data centers (physical security controls)
By clearly outlining these areas, the IT department (servers, networks, databases), HR processes (background checks, employee onboarding), and data centers (physical security controls), you have drawn a precise boundary.
Step 2: Form a Gap Analysis Team
Trying to tackle ISO 27001 alone is like trying to lift a car by yourself; it is just not going to happen efficiently, and you might hurt yourself in the process. You need a team, a diverse group of individuals who bring different perspectives and expertise to the table. Build a multidisciplinary team involving key stakeholders. Team members typically include:
- Information Security Officer (ISO) (Team Lead)
- IT Manager/System Administrators (Technical Assessment)
- HR Manager (Policy and Training)
- Compliance Officer (Regulatory Requirements)
- External Consultant (Independent Validation) (Optional)
Step 3: Identify Applicable ISO 27001:2022 Requirements
The ISO 27001:2022 standard is your blueprint. You can not build a secure fortress if you do not understand the specifications. This step is about dissecting the standard and pinpointing what truly applies to your organization based on your defined scope. Review the standard and identify which clauses and controls apply to your organization. Relevant requirements:
- Context of the organization (Clause 4): This is about understanding your business environment, stakeholders, and their expectations regarding information security. It is setting the stage.
- Leadership (Clause 5): Crucial! Top management must be on board, demonstrating commitment and establishing the information security policy. Without leadership buy-in, your efforts will likely fall flat.
- Planning (Clause 6): This is where you identify risks and opportunities related to information security and plan how to address them. It is your strategic roadmap.
- Support (Clause 7): This covers the resources you need, including people, infrastructure, communication, and crucially documented information.
- Operation (Clause 8): This is where the rubber meets the road, implementing and controlling the processes needed to meet your information security objectives.
- Performance evaluation (Clause 9): You can not improve what you do not measure. This clause focuses on monitoring, measuring, analyzing, and evaluating your ISMS.
- Improvement (Clause 10): Continuous improvement means taking corrective actions and constantly looking for ways to enhance your information security management system.
- Annex A controls (93 controls in 4 themes, Organizational, People, Physical, Technological): This is the treasure trove of specific security controls. Based on your risk assessment, you must carefully consider which of these 93 controls are relevant and necessary for your organization.
Step 4: Assess Current State vs. ISO Requirements
This is where your team puts on their detective hats and starts digging into your current practices. They compare these practices against the ISO 27001:2022 requirements you’ve identified. Assessment methods include:
- Interviews and questionnaires
- Document and policy reviews
- Direct observations/site visits
Example:
- Control A.5.1: “Information Security Policy”:
- Requirement: A defined policy communicated across the organization.
- Current state: Policy exists, but employees are unaware of its content.
- Gap: Communication and policy training are insufficient.
- Control A.8.2 – Privileged Access Rights:
- Requirement: Access rights must be restricted, managed, and reviewed regularly.
- Current state: Privileged access reviews are performed irregularly and are undocumented.
- Gap: Lack of a formal, periodic, and documented privileged access review process.
Step 5: Document Gaps Clearly
Once you have unearthed those gaps, you must document them clearly and systematically. Gap documentation should include:
- ISO clause/control
- Description of the gap
- Potential impact/risk
- Priority (High, Medium, Low)
Example: Gap Analysis Sheet
| ISO Clause/Control | Current State | Gap Identified | Impact/Risk | Priority |
| A.5.1 – Policies for information security | Policy exists, but is not communicated to staff | Lack of policy awareness across teams | Noncompliance and inconsistent practices | High |
| Annex A.7.4 – Physical Security Monitoring | No visitor logs are maintained in the data center | No monitoring or logging of physical access | Risk of unauthorized access to secure areas | High |
| A.8.9 – Configuration management | Devices configured ad-hoc without standard baselines | No formal configuration management process | System vulnerabilities due to misconfigurations | Medium |
Step 6: Develop a Remediation Action Plan
Identifying the problems is only half the battle; you need a plan to fix them. Your remediation action plan is your roadmap to closing those gaps and achieving ISO 27001:2022 compliance. Create a detailed roadmap to close each gap. Your plan should include:
- Action items
- Responsible parties
- Timeline
- Expected outcome
| Gap Identified | Corrective Action | Responsible | Timeline | Outcome |
| Employees are unaware of the InfoSec Policy | Conduct mandatory training sessions | HR Manager, ISO | 2 months | Increased awareness and policy adoption |
| No access review policy | Implement a quarterly review process | IT Manager | 3 months | Documented and regular access checks |
| Outdated documents | Create a version control system and update policies | Compliance Officer | 1 month | Accurate and up-to-date documentation |
Step 7: Implement Corrective Actions and Monitor Progress
The plan is in place; now it is time for execution. This step involves implementing your remediation actions and, crucially, monitoring your progress. Things do not always go as planned, so regular check-ins are essential. Monitoring tools include:
- Weekly or monthly progress reviews
- Project tracking systems (e.g., Jira, Asana)
- Management updates
Step 8: Conduct Follow-Up Reviews
Once you have implemented the corrective actions, you can not just assume the gaps are closed. You need to verify! Follow-up reviews are essential to ensure that the actions taken have been effective and the gaps are closed. Verification methods:
- 3 months post-remediation
- Internal audit confirms training completion
- Access reviews, documents, and running
- Policies updated and version-controlled
Step 9: Document Final Gap Analysis Report
Finally, you need to compile all your findings, actions, and outcomes into a comprehensive gap analysis report. This document serves as a record of your journey, highlighting where you started, the gaps you identified, the steps you took to close them, and your current state of compliance. Final Report Includes:
- Executive summary
- Gap findings and action steps
- Post-remediation status
- Suggestions for continuous improvement
ISO 27001 Training with InfosecTrain
An ISO 27001 gap analysis is the single most valuable step you can take before committing to implementation or certification. It provides clarity, builds alignment, and puts you in control of your cybersecurity narrative. Do not treat it like an Administrative task. Done right, it can be the spark that ignites a full transformation in your organization’s management of risk, trust, and resilience.
Remember: The biggest risk is not finding a gap. It is not knowing it is there.
If you are ready to bridge those gaps with confidence and accelerate your ISO 27001 journey, InfosecTrain’s ISO 27001 Lead Implementer and Lead Auditor training courses are smart choices. Whether you are leading the implementation or just getting started, these courses equip you with the knowledge, tools, and real-world strategies to achieve compliance and maintain security.
Start your training today with InfosecTrain. Because knowing what to do next makes all the difference when it comes to security.
TRAINING CALENDAR of Upcoming Batches For ISO 27001 : 2022 LA
| Start Date | End Date | Start - End Time | Batch Type | Training Mode | Batch Status | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 28-Feb-2026 | 29-Mar-2026 | 19:00 - 23:00 IST | Weekend | Online | [ Open ] | |
| 04-Apr-2026 | 03-May-2026 | 09:00 - 13:00 IST | Weekend | Online | [ Open ] |

